Numpy Cheatsheet for Beginners–Arrays, Slicing, Reshape, Axis and More
When I first started learning data science and machine learning with Python, I kept bumping into Numpy. The documentation was solid but too dense for quick learning. I needed a clear, simple reference with code-first explanations. That’s why I made this guide—for people like me who just want to get things done and understand the basics quickly.
Getting Started with Numpy
Numpy is a fast, memory-efficient library that enhances Python lists by supporting multi-dimensional arrays and matrix operations.
Array Creation and Indexing
import numpy as np
# One-dimensional array
a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
a[0] # 1
a[-1] # 3
a[0:2] # array([1, 2])
# Two-dimensional array
a2 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
a2.ndim # 2
# Define data type
a3 = np.array([1, 2, 3], dtype=np.float64)
Elementwise Operations
a1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
a2 = np.array([4, 5, 6])
a1 + a2 # array([5, 7, 9])
a2 - a1 # array([3, 3, 3])
a1 * a2 # array([4, 10, 18])
a1 / a2 # array([0.25, 0.4 , 0.5 ])
Matrix Multiplication
a3 = a2.transpose()
a1.dot(a3)
Matrix Shape and Slicing
a = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
a.shape # (3, 2)
a[0:2, 1] # array([2, 4])
a[:, 1] # array([2, 4, 6])
a.reshape(2, 3) # reshape to 2x3 matrix
Axis Concept
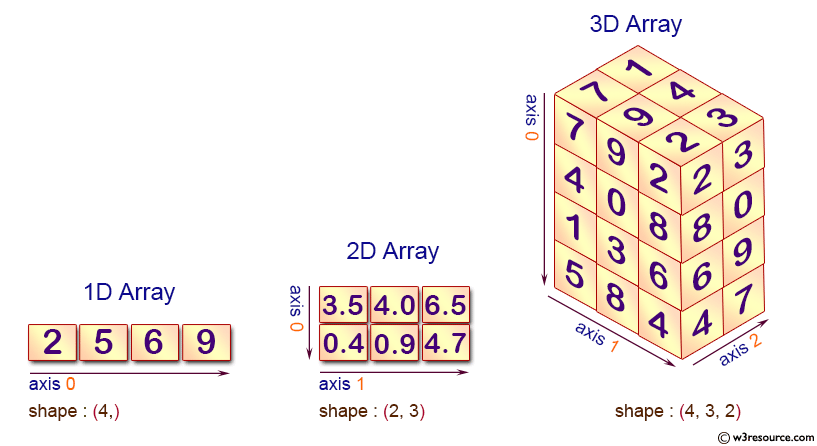 Understanding axis is crucial:
Understanding axis is crucial:
- axis=0 → column-wise operation (down the rows)
- axis=1 → row-wise operation (across the columns)
Numpy Methods Cheatsheet
Array Generators
np.arange(0, 10, 2) # Like Python's range
np.zeros((3, 4)) # 3x4 matrix of zeros
np.ones((3, 4)) # 3x4 matrix of ones
np.eye(2) # 2x2 identity matrix
np.random.random((2, 2)) # 2x2 matrix with random values
np.linspace(0, 1, 5) # Five values linearly spaced between 0 and 1
Common Operations
np.sqrt(a) # Square root
np.std(a) # Standard deviation
np.unique(a) # Unique values
np.vstack((a, b)) # Vertical stack
np.hstack((a, b)) # Horizontal stack
Object Methods
a.ravel() # Flatten array
a.min() # Minimum value
a.max() # Maximum value
a.sum(axis=0) # Column-wise sum
a.sum(axis=1) # Row-wise sum
a.transpose() # Transpose
Array Properties
a.size # Total number of elements
a.ndim # Number of dimensions
a.dtype # Data type
a.itemsize # Size of each element in bytes
a.shape # Tuple of row and column count
Vectorized Operations
a = np.arange(6).reshape(3, 2)
b = a > 3
c = a[b] # Filter elements > 3
a[b] = -1 # Replace elements > 3 with -1
Iteration with nditer
a = np.arange(6).reshape(3, 2)
# Row-major (C-style)
for x in np.nditer(a, order='C'):
print(x)
# Column-major (Fortran-style)
for x in np.nditer(a, order='F'):
print(x)
vstack vs hstack
a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
b = np.array([4, 5, 6])
np.vstack((a, b))
# Output: [[1 2 3], [4 5 6]]
np.hstack((a, b))
# Output: [1 2 3 4 5 6]
Final Words
This cheatsheet isn’t meant to cover every advanced Numpy feature, but it’s built to give you a solid starting point. Bookmark it, refer to it, and play around with the code. That’s how I learned Numpy—and it worked.
If you found this helpful, consider sharing it with someone who’s just getting started in Python or data science.
👋 About Me
Hi, I’m Shuvangkar Das, a power systems researcher with a Ph.D. in Electrical Engineering from Clarkson University. I work at the intersection of power electronics, DER, IBR, and AI — building greener, smarter, and more stable grids. Currently, I’m a Research Engineer at EPRI (though everything I share here reflects my personal experience, not my employer’s views).
Over the years, I’ve worked on real-world projects involving large scale EMT simulation and firmware development for grid-forming and grid following inverter and reinforcement learning (RL). I also publish technical content and share hands-on insights with the goal of making complex ideas accessible to engineers and researchers.
📺 Subscribe to my YouTube channel, where I share tutorials, code walk-throughs, and research productivity tips.







Leave a comment